Is Drinking Coffee Beneficial for Your Health?
Is coffee beneficial or harmful to your health? What are the actual health benefits of drinking coffee? Are these benefits based on science or just myths?
Every month, thousands of people search for answers to these questions on Baidu. It’s clear that understanding the health impacts of coffee is important. This article aims to provide clarity. We will delve into some of the potential health benefits of coffee and examine scientific studies that support these claims. By the end of this article, you should be able to answer the question: “Is coffee good for you?”
The Marvelous Coffee Cherries
Few would argue against the idea that having a cup of coffee is an excellent way to wake up and feel refreshed, especially first thing in the morning.
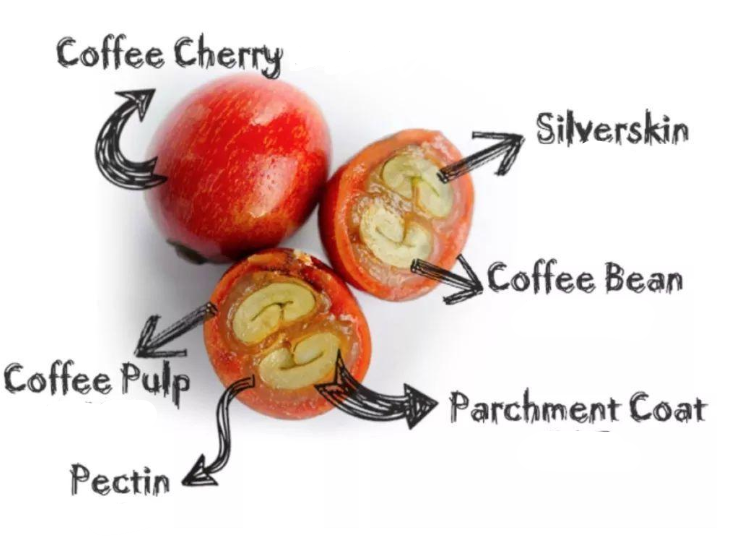
Coffee comes from the seed of a berry called a coffee cherry that grows on coffee plants. Legend has it that an Ethiopian shepherd named Kaldi discovered these beans when he noticed his goats became unusually energetic and refused to sleep after eating berries from a particular tree (can you guess which one)? Monks from a nearby monastery heard about this discovery and started roasting and grinding these beans before soaking them in water. They soon realized that this new drink helped them stay awake during their long prayers.
However, there is no historical evidence to back up this charming little story.
In his book “Coffee: A Dark History,” Tony Wild recounts another story with some indirect evidence. Mohammed bin Sa’id al-Dhabhani is credited as being the “inventor” of brewed coffee about 560 years ago. It’s said that Mohammed bin Sa’id al-Dhabhani—also known as Gemaleddin—traveled from Aden to Ethiopia as a missionary and brought back some coffee fruits. Initially, he tried brewing with dried leaves from these fruits (a technique he picked up from Chinese tea practices). But he didn’t stop there; he also brewed using the pulp of the actual coffee cherries themselves, finding this method produced a tastier drink compared to just using dried leaves. This could be considered the origin of Yemen’s traditional hot beverage Qishr.
This exotic drink quickly gained popularity; by the 15th century, coffeehouses had become common in Iran, Turkey, and across the Arab world. These establishments were not only places for cultural and artistic discussions but also venues for merchants to talk business.
By the 16th century, coffeehouses were thriving in cities like Venice, London, and Paris. In America, Boston saw its first coffeehouse open in 1689. Today, this culture continues to thrive worldwide.
Coffee truly represents a global culture

Coffee ranks as the third most consumed beverage globally, right after water (first) and tea. While some might dismiss it as “just another drink,” you’ll soon see that it’s far more than that. Coffee carries an inherent allure and mystery. For over 560 years, it has played a significant role in human history—featuring in legends, conspiracies, debates, attacks, and politics alike. Naturally, it’s also woven into our daily routines.
Economically speaking, coffee offers substantial benefits but can also spark contentious environmental and social issues. Over time, a rich global culture around coffee has emerged. Our goal isn’t necessarily to become experts but to savor the myriad flavors, aromas, and nuances that our coffee presents us with daily. Beyond its well-known qualities, recent findings reveal that drinking coffee comes with some surprising health benefits.
Is Coffee Good for Your Health?

Each year brings new scientific discoveries about the surprising health benefits of drinking coffee—some might even shock you! A few years ago, international research institutions reviewed numerous studies on how coffee affects various diseases and concluded that it offers many potential health advantages. Is drinking coffee good for your health? Let’s delve into some of these benefits to find out.
By the way, most studies focus on black coffee.
1.Liver Protection
The liver is an extraordinary organ tasked with filtering blood from your digestive tract, processing fructose and alcohol, detoxifying harmful chemicals, and aiding in the metabolism of over-the-counter (OTC) medications. According to a 2017 article by Xiao in Hepatology journal, drinking coffee can lower your chances of developing cirrhosis. Another pioneering study conducted by Setiawan in 2015 at Keck School of Medicine revealed that compared to non-coffee drinkers:
- Drinking 2-3 cups daily reduces chronic liver disease (CLD) mortality risk by 46%
- Drinking 4 or more cups daily reduces CLD mortality risk by 71%
As shown here, higher coffee consumption correlates with a lower risk of CLD—a clear inverse relationship between coffee intake and these diseases. Researchers also discovered that this “inverse association was consistent regardless of participants’ race, gender, body mass index (BMI), smoking status, alcohol consumption or diabetes status.” Heath & Nieber’s studies from 2017 also indicated that coffee lowers risks associated with cirrhosis, fibrosis, viral hepatitis, and cancer. The impact is so significant that some refer to it as “the magic bean for liver disease.” If you’re keen on understanding how coffee affects liver disease (or other conditions) and can navigate scientific literature well enough to interpret it accurately—then visiting the Institute for Scientific Information on Coffee (ISIC) would be beneficial. This organization serves as a key resource for research on how coffee impacts health; we’ll reference their findings frequently throughout this article. Specifically notable is ISIC’s comprehensive list detailing how coffee influences liver function.
Keep in mind that scientific findings can sometimes be complex or contradictory; some studies might show positive effects while others do not—that’s just part of how science works.
2.Lowering Cancer Risk
The Amazing Coffee Cherry
Cancer involves the uncontrolled growth of cells. While there are many different types of cancer and it’s inaccurate to claim that coffee can treat all forms, some positive findings have emerged regarding certain cancers. According to Setiawan&2015:
- Drinking 2-3 cups of coffee daily can lower the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) by 38%.
- Consuming 4 or more cups per day can reduce liver cancer risk by 41%.
Coffee is also thought to decrease the risk of colorectal cancer, female breast cancer, hepatocellular carcinoma, and head and neck cancers. Interestingly, in 1991, the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) classified coffee as “possibly carcinogenic to humans.” However, during a meeting in 2016, IARC revised this classification to “not classifiable,” suggesting that coffee is now considered safe and potentially beneficial. This article explores these findings! The ISIC provides a comprehensive list of studies on how coffee impacts various types of cancer.
3.Helps You Live Longer

The benefits highlighted in this article suggest that coffee might help extend your lifespan by preventing adverse health events like cancer. While coffee isn’t a magical cure for immortality, it can contribute to lowering your mortality rate. Studies indicate that drinking coffee reduces the risk of death from cardiovascular disease, cancer, stroke, diabetes, and respiratory and kidney diseases among African Americans, Japanese Americans, Latinos, and Whites.
Daily coffee drinkers who consume one cup a day have approximately a 12% lower risk of dying from various diseases such as cancer, stroke, heart disease, and diabetes. Those who enjoy around three cups daily can reduce their mortality risk by about 18%.
4.Enhances alertness and energy levels
Sometimes we all need an energy boost. Whether it’s students pulling all-nighters, working shifts, or just getting up early, coffee can be your ally! A neurotransmitter called adenosine affects brain cells by inhibiting memory, mood, and reaction time, making you feel sleepy.
Coffee blocks adenosine and essentially “wakes you up,” which is why we feel so refreshed and invigorated after having a cup.
A daily cup of coffee makes life more enjoyable.
5.Prevents cavities

Many of us might be aware that drinking black coffee can make our teeth lose their shine. However, consuming strong black coffee can actually kill bacteria that would otherwise stick to our teeth and cause cavities (Nambodiripad & Kori 2009). Additionally, Yadav (2017) discovered that using green coffee bean extract as a mouthwash can significantly reduce the number of Streptococcus mutans, a common oral bacterium responsible for cavities.
While coffee might dull your teeth’s appearance, it helps in keeping them healthy and intact for a longer time!
6.Reduces the risk of heart attack
A heart attack happens when blood flow to part of the heart is obstructed. Drinking coffee can help lower the risk of coronary heart disease. Consuming at least 3 cups of coffee daily can also decrease the likelihood of cardiovascular complications following a heart attack. The ISIC (Institute for Scientific Information on Coffee) provides a comprehensive list of studies on how coffee impacts cardiovascular health.
Drinking coffee regularly helps maintain your heart’s performance!
7.Reducing Stroke Risk
A stroke occurs when blood vessels supplying the brain become blocked or burst open. Research by Lee in 2007 from Korea indicated that drinking coffee helps prevent strokes in middle-aged women, though not in men. That might sound like bad news for men, but hold on! There’s more… A study by Kokubo in 2013 from Japan found that people who drink 1 to 2 cups of coffee daily, or even 2 to 6 cups weekly, have a reduced risk of stroke. These findings apply to the “general population,” which includes men!
So, is coffee good for you? Yes, both men and women can lower their stroke risk by drinking coffee.
8.Lowering Risk of Parkinson’s Disease
Parkinson’s Disease is a progressive disorder affecting the central nervous system. It harms nerve cells in the brain and inhibits dopamine production. While Parkinson’s isn’t typically fatal, it severely limits mobility as symptoms progress. Research by Yamada-Fowler in 2014 at Linköping University in Sweden found that drinking coffee reduces the risk of developing Parkinson’s Disease.
The ISIC also offers an extensive list of studies on how coffee affects Parkinson’s Disease.
9.Preventing Alzheimer’s Disease

Alzheimer’s disease is another neurodegenerative condition and stands as the leading cause of dementia worldwide. While it typically affects those over 65, there are steps you can take to shield yourself from this ailment—drinking coffee being one such measure.
Studies by Eskelinin & Kivipelto (2010) and Ross (2000) suggest that regular coffee consumption can lower the risk of Alzheimer’s disease and slow cognitive decline. Although Panza (2015) is less conclusive, it doesn’t dismiss potential benefits.
So grab a cup of coffee daily; it might just keep you safe!
10.Lowering Risk for Type 2 Diabetes (Adult-Onset Diabetes)
Research from Harvard University by Ding (2014) discovered that a daily cup of coffee could cut diabetes risk by up to 8%.
Interestingly enough, they found similar benefits with decaffeinated coffee too, indicating that other compounds in coffee—not just caffeine—play a role in this effect. If you’re already diagnosed with diabetes, it’s not too late either. A study by Bidel (2006), spanning two decades on type 2 diabetes patients, revealed that regular coffee drinkers had nearly a 30% lower mortality rate. Yes, these researchers waited precisely 20.8 years to compile their findings—talk about dedication! An analysis by Carlström & Larsson (2014) at Karolinska Institute covering around 30 previous studies also supported the idea that coffee reduces type 2 diabetes risk.
A daily dose of coffee could help regulate your blood sugar levels!
11.Preventing Kidney Stones
When minerals concentrate in urine, they form tiny yet excruciatingly painful stones that either lodge in your kidneys or pass through your ureters—neither scenario being pleasant. The issue with kidney stones is they only manifest symptoms once they start moving within your kidneys. And no, an ice pack won’t alleviate this pain.
Luckily, Ferraro (2014) found that drinking at least one cup of coffee each day could reduce kidney stone risk by 26%. Yet science often comes with contradictions; Sun (2019) showed caffeine intake was “linked to a higher recurrence risk for kidney stones in adults,” particularly among non-Caucasian women who aren’t overweight. But don’t lose hope—future research might uncover more positive aspects regarding coffee and kidney stones. Lastly, ISIC highlighted studies showing caffeine might also lower gallstone risks.
Coffee: It moves mountains—and stones!
12.Burning Fat and Losing Weight

There’s a solid reason why every commercial weight loss supplement includes caffeine: Koot & Deurenberg (1995) discovered it can boost human metabolic rate by 11%. Jeukendrup & Randell (2011) reviewed various effects of caffeine on metabolism, with some studies showing that caffeine significantly increases resting metabolic rate. They concluded: “According to current literature, there is evidence supporting the fat-metabolizing properties of caffeine and green tea.” Coffee aids in weight loss. However, don’t toss out your running shoes or abandon a healthy diet just yet.
A cup of coffee a day keeps the fat at bay?
13.Enhances Cognitive Function
We all want to be a bit smarter, and coffee might help you achieve just that.
Borota et al. (2014) found that individuals who consumed 200 milligrams of caffeine (a bit more than what’s in an average Starbucks cup) had better long-term information retention. We all know how tough it can be to get up in the morning. This is especially true for college students who often wake up late because it’s their “non-optimal” time of day. However, Sherman et al. (2016) discovered that coffee improved these young adults’ memory—a big help for morning exams! Caffeine blocks adenosine, a neurotransmitter that inhibits norepinephrine, which is another neurotransmitter aiding memory retention. So next time you’re cramming for an exam late at night (or early in the morning), drinking a cup of coffee offers dual benefits—keeping you focused and boosting your memory.
ISIC has published another report on studies examining coffee’s impact on mental performance.
Drinking a cup of coffee daily is smart!
14.Prevents Retinal Degeneration
Retinal degeneration refers to the gradual deterioration of the retina in your eyes. The retina, located at the back of your eye, captures images and sends them to your brain through the optic nerve. This condition occurs as retinal cells slowly die off. Several factors can contribute to retinal degeneration, including an unhealthy diet, prolonged exposure to intense light, and iron deficiency.
According to a 2014 study by Jang from Cornell University: “…drinking coffee might help in preventing retinal degeneration.”
15.Lowering melanoma risk

Melanoma is a type of cancer that originates from pigment-producing cells known as “melanocytes.” This form of cancer can spread quickly and can be life-threatening. According to Loftfield (2015), consuming four cups of coffee daily is linked to a “modest reduction in melanoma risk.” While it’s not yet clear if drinking coffee can prevent further progression of melanoma in cancer patients, it shows promise. Although I could have included this information in the general cancer section, I believe melanoma warrants its own dedicated part.
Coffee might help, but don’t forgo sunscreen
16.Combating Depression

Depression is a serious mental health disorder and has become an increasingly significant issue worldwide, including in the United States. In 2017, it was estimated that around 7% of American adults (approximately 117 million people) experienced at least one major depressive episode. Depression can greatly diminish one’s quality of life; thus, finding anything helpful is crucial.
A study by Lucas et al., conducted in 2011 with 50,739 American women participants, revealed that those who consumed four or more cups of coffee daily over ten years had around a 20% reduced risk of developing depression. The study also noted that decaffeinated coffee did not have any impact on depression—another reason to skip the decaf!
Furthermore, research by Kawachi et al., published in 1996, indicated that women who drank four or more cups of coffee daily were 53% less likely to commit suicide. Men aren’t left out either; according to Ruusunen et al., published in 2010, men who consumed large quantities of coffee (about three to four cups per day) had a lower risk of depression compared to those who didn’t drink coffee.
So if you’re dealing with depression, could coffee be beneficial for you? The outlook seems positive—you might even consider it your liquid “happy pill.”
17.Provides Essential Nutrients
Coffee beans are packed with beneficial nutrients.
While some nutrients are lost during processing, many still make it into your cup.
An average cup (8 ounces) of regular coffee contains:
- 0.2 mg Vitamin B2 (riboflavin), approximately 11% Daily Value (DV)
- 0.6 mg Vitamin B5 (pantothenic acid), approximately 6% DV
- 0.5 mg Vitamin B3 (niacin), approximately 2% DV
- 4.7 µg Vitamin B9 (folic acid), approximately 1% DV
- 116 mg potassium, approximately 3% DV
- 0.1 mg manganese, approximately 3% DV
- 7.1 mg magnesium, approximately 2% DV
These figures might seem modest at first glance, but many people consume multiple cups daily—meaning these values can add up quickly! Think of it like green tea; you can view your daily brew as a nutritional supplement without needing pills.
Is coffee beneficial for your nutrition? Absolutely.
18.Perks You Up

Coffee has psychological effects and is considered a psychoactive drug. Caffeine might be the most widely consumed psychoactive substance globally, and it’s legal!
Chan & Maglio (2019) discovered that our connection between coffee and alertness is so deep-rooted that merely thinking about brewing it can be enough to wake you up!
Haskell-Ramsay (2018) performed a series of tests 30 minutes after consuming 220 ml of regular coffee containing 100 mg of caffeine. These tests measured alertness, mood, headache, fatigue, mental fatigue, and nervousness. They found that coffee:
- Shortened reaction time (compared to a placebo—a “fake” coffee drink)
- Increased alertness (compared to a placebo—a “fake” coffee drink)
- Reduced fatigue (compared to decaf coffee)
- Reduced headaches (compared to decaf coffee)
- Stimulated nerves
Interestingly, they also discovered that decaf coffee boosted alertness. This suggests that the impact of coffee might come from other molecules in the brew rather than just caffeine. If you’re interested, ISIC offers an expert review on how coffee affects mood and emotions.
The takeaway message is that drinking up to 4 cups of coffee daily can keep you alert and happy throughout the day! So, is coffee good for you? Yes!
19.Enhance physical performance

Can coffee serve as a “stimulant” boosting athletic performance? As we’ve seen it can enhance physical functions though its societal acceptance means its effects are modest at best. So yes—coffee benefits both your health and athletic performance!
In sports caffeine (and by extension coffee) isn’t typically banned which is great news if you’re both an athlete and a fan of java!
20.Preventing Kidney Disease
Your kidneys play crucial roles removing cellular waste acids excess fluids balancing water salts minerals (like sodium potassium) producing hormones controlling blood pressure generating red blood cells strengthening bones.
When kidneys fail chronic kidney disease ensues spreading silently often undetected initially caused by damaged nephrons—the structures filtering waste from blood leading wastes fluids accumulating causing severe bodily harm permanent kidney damage if unresolved.
Jhee & 2018 concluded daily single-cup coffee drinkers face lower kidney disease risks compared non-drinkers making a strong case for its benefits: Drink Coffee -> Happy You -> Happy Kidneys!
21.Key Source of Antioxidants
Packed with antioxidants crucial for cell protection against free radicals reactive oxygen species (ROS), seemingly paradoxical given oxygen’s necessity yet potential toxicity via ROS; these tiny dangerous entities attacking proteins DNA lipids causing diseases if unchecked arising internally externally via environment radiation exposure.
Thankfully antioxidants—molecules within us—combat ROS/free radicals collaboratively involving proteins enzymes small molecules like vitamins C E though dietary supplements become necessary when depleted internally.
Here’s where coffee shines containing chlorogenic acid melanoidins among others acting as potent antioxidants; Norwegian studies even showed adults’ primary antioxidant source being—surprisingly—coffee! A boon for veggie-averse folks merely needing their caffeine fix though alternatives like tea fruits exist should both veggies java displease—which would indeed be tragic survival-wise!
So—is Coffee Beneficial? Absolutely with its rich antioxidant profile being advantageous undeniably though unlike essential vitamins dietary avoidance remains feasible.
22.Enjoyment

We’ve already seen how our physical and mental well-being can benefit from drinking coffee. However, it’s important to remember that coffee isn’t a medication meant to be consumed two, three, or four times a day—no matter who you are or where you are. One final benefit of drinking coffee is…
You enjoy it!
How Does Coffee Work?
How does coffee impact our cells in so many different ways? Currently, there’s no definitive answer as research continues. Studying this is challenging because there are over a thousand different molecules in coffee—and caffeine isn’t always the main active ingredient. Coffee’s effects could come from one or more other molecules working alone or together. Various factors influence the molecular makeup of your cup of joe:
- The type of coffee plant (e.g., Arabica or Robusta)
- Growing conditions (soil quality, climate, altitude)
- Harvesting methods (hand-picked vs machine-picked)
- Processing techniques (dry vs wet processing)
- Storage and transport conditions
- Roasting levels (light roast vs medium roast vs dark roast)
- Grinding coarseness (coarse vs medium vs fine grind)
- Brewing methods (drip brew vs espresso vs siphon brewing)
- Additives like milk or sugar
Each step impacts your final cup’s composition—meaning your cup might have more beneficial compounds than someone else’s—or less! Individual differences also play a big role; what works wonders for one person might not work at all for another.
Given these factors and the sheer number of compounds in each bean, it’s clear why researching coffee’s effects is so complex and challenging.
Is Coffee Bad for You?
Can drinking too much be harmful? Yes—especially if you’re sensitive to caffeine. We also advise caution with concentrated supplements like caffeine pills or powders; while they’re generally safe in moderation, too much isn’t better. Overconsumption can lead to headaches, stomach issues like diarrhea and indigestion, heartburn, reflux—and more.
So yes—coffee can be bad for some people.
Is Coffee a Fruit?
Coffee comes from the seeds of the coffee cherry (also known as the coffee berry) which grows on the coffee tree. Each cherry contains pulp and other layers along with two seeds. These seeds are what we call coffee beans. So technically, while coffee beans are part of a fruit, they aren’t considered an entire fruit themselves.
Tea vs Coffee: Which Is Better?
I’m not biased; tea definitely has its own benefits.
However, when it comes to nutrition and other health advantages, coffee seems to have an edge over tea.
That said, drink whatever you enjoy. I like both but have a preference for coffee.
What’s the Best Way to Drink Coffee?
The best way is through your mouth. I’ve heard about coffee enemas but never felt compelled to try them. Okay… I assume you’re asking about brewing methods? Well, that’s also a matter of personal preference. Different brewing techniques will give you varied flavors and aromas.
Feel free to experiment and find out what works best for you.
Are Coffee Beans the Same as Mung Beans?
Coffee beans are not the same as mung beans; they come from different plant families.
Specifically, coffee beans come from plants in the Rubiaceae family while mung beans belong to the Fabaceae family.
