8 health benefits and 6 health disadvantages of coffee
Coffee is a staple beverage in nearly every American household, ranking as the second most consumed drink globally. Due to its widespread consumption, extensive research has been conducted on its health benefits and potential drawbacks. Essentially, coffee embodies the adage: “Moderation is key.” While moderate consumption can be beneficial, excessive intake may lead to hypersensitivity, prompting some to consider switching to tea. Let’s explore the polarized benefits and notable drawbacks of drinking coffee daily.
Health Benefits of Coffee
Starting with the positives, here are some reasons why you should consider drinking coffee. These benefits range from fighting diseases and medical conditions to reducing inflammation and pain. Interestingly, it’s a favorite among athletes and sleep-deprived college students.
1.Reduces Risk of Type II Diabetes
Coffee offers multiple ways to help combat Type II diabetes. One of the most beneficial aspects of the chlorogenic acids found in coffee is their effect on insulin secretion and metabolism acceleration, which speeds up food breakdown. You might notice a reduction in glucose levels by about 30%, meaning your pancreas doesn’t have to work as hard to regulate blood sugar levels. While there are many polarized articles and studies regarding coffee’s impact on cardiovascular diseases, it’s crucial to understand the standards behind these studies. Researchers at Harvard University have found that these studies also account for reductions in liver disease and cardiovascular issues. Coffee benefits cardiovascular health but has varying effects on obese adults, individuals with arrhythmias, or those allergic to caffeine. When you drink coffee, your pancreas doesn’t need to produce as much insulin; additionally, it acts as a diuretic helping you urinate and expel toxins from your body.
2.Anti-inflammatory drugs aid in treating rheumatoid arthritis
Antioxidants are present in every single coffee bean; they are what make coffee so remarkable. These antioxidants act like rocket fuel for your immune system and body by combating free radicals known to cause cancer and various other diseases.
If you’re looking for an excuse to drink more coffee: having two cups a day provides ample antioxidants through its chlorogenic acids content. Green coffee beans are believed to contain higher amounts of chlorogenic acid; however, the roasting process chemically alters them making them easier for our bodies to metabolize.
For those suffering from rheumatoid arthritis where Tylenol offers no relief, antioxidants naturally serve as anti-inflammatory agents without any artificial ingredients or liver-damaging properties.
Since coffee metabolizes quicker than stubborn capsules, its relief may be short-lived. However, if you’ve had a challenging day dealing with joint pain, it’s just another reason for an extra cup.
3.Supports heart tissue

If you’re unfamiliar with the p27 protein, you’re not alone; we were too before diving into this research. The p27 protein regulates the cell cycle, which is a series of biochemical steps that control cell growth and division.
Exciting new research indicates that caffeine has a novel role in heart protection. It stimulates p27 to enter the mitochondria, the energy centers of heart cells, triggering a series of events that shield the myocardium from damage.
4.Enhances spatial awareness through stimulation

We all know that drinking coffee can make us feel jittery, but most of us aren’t aware of why this happens. It’s because coffee increases our awareness of our surroundings and actually enhances our cognitive functions. This effect can last quite a long time, typically between three to five hours.
After being metabolized by the liver in about 45 minutes, caffeine stays in the bloodstream for up to around nine hours. During these subsequent hours, even though caffeine remains in your blood, its cognitive effects diminish until there’s no noticeable difference from your usual state.
Besides providing mental stimulation through caffeine, drinking coffee can also lower the risk of suicide or suicidal thoughts. Everyone reacts slightly differently to coffee; while it enhances time perception and overall spatial awareness, consuming too much can lead to irritability.
Incorporating an appropriate amount of coffee into your routine provides a healthy and natural mental boost.
5.Combatting Parkinson’s Disease and Alzheimer’s Disease

Around the world, we’ve consumed an impressive amount of coffee—about half a trillion cups. Researchers have discovered a link between coffee consumption and Parkinson’s disease. A team of experts investigated this connection further and found that phenylindanes, which are more commonly found in dark roasted coffee, can prevent certain compounds from “clumping together.” When these compounds accumulate in our bodies, they can lead to Parkinson’s disease and Alzheimer’s disease.
Remarkably, this is the first time anyone has associated phenylindanes with preventing the proteins responsible for these two debilitating diseases.
These discoveries also highlight other genetic factors influenced by phenylindanes concerning various diseases and medical conditions, such as type II diabetes and cardiovascular diseases previously mentioned.
6.Aid in breaking down fat cells
This isn’t breaking news. Since the 1980s, science has recognized that caffeine significantly aids in weight loss. Over time, consuming caffeine before exercising can shrink fat cells by nearly 25% and help reduce excess body weight by 22%.
As a muscle-stimulating agent, caffeine is believed to allow deeper fat burning during workouts compared to standard exercises. It’s worth noting that these studies reviewed everything over extended periods and focused on aerobic exercises rather than strength training. While both aerobic and strength training are key components of modern fitness routines, combining aerobic exercise with caffeine—especially when aiming for substantial weight loss—can significantly enhance your progress.
Consider this: if you’re set to lose 30 pounds over 90 days but take caffeine before each workout session, you could potentially shed an extra 6 pounds.
7.Cancer Prevention
Cancer involves uncontrolled cell growth occurring throughout your body in specific ways. With numerous types and causes of cancer known today, coffee can play a role in keeping it at bay for as long as possible. This benefit boils down to polyphenols (also antioxidants) present in coffee beans; their effects vary based on roasting and processing techniques.
For instance, Swiss water-processed decaf beans might have similar polyphenol levels as regular light roast caffeinated beans; however, beans processed via indirect or direct solvent methods may contain fewer polyphenols.
Interestingly enough, darker roasts boast higher polyphenol content due to shorter roasting times required. Online searches might yield claims suggesting dark roast caffeine is carcinogenic; however, one study indicates that caffeine in coffee isn’t yet classified as a carcinogen.
Additional research points out that caffeine might lower risks for certain cancers—specifically liver cancer, colorectal cancer, and prostate cancer—with dark roasts containing more anti-cancer polyphenols disrupting cell cycle processes linked to various cancers’ development.
Lastly—and recalling our earlier mention—the P27 protein also plays a role here: lower levels correlate with increased cancer risks due to reduced inhibition of cancer cell production.
8.Alleviate Constipation

While it may be an unpleasant topic, drinking coffee can indeed help alleviate constipation.
Caffeinated coffee can stimulate your colon muscles, and even decaffeinated coffee along with its metabolic process can influence your colon, thus easing constipation. Apart from muscle stimulation, the magical nectar of coffee (chlorogenic acid) also triggers receptors in the stomach to produce acid.
Essentially, drinking coffee speeds up food digestion partly because it boosts metabolism.
The Health Downsides of Coffee
Coffee is fantastic—we’ve already discussed some benefits—but there are additional factors to consider. If everything were perfect, we’d solve all issues just by consuming coffee extract. However, one problem with coffee—or more precisely caffeine—is that it may cause overstimulation. This is particularly true if you are sensitive to caffeine. Some effects vary by individual circumstances, but it’s crucial to understand all facts before incorporating coffee into your diet as a health staple.
1.Elevated Blood Pressure
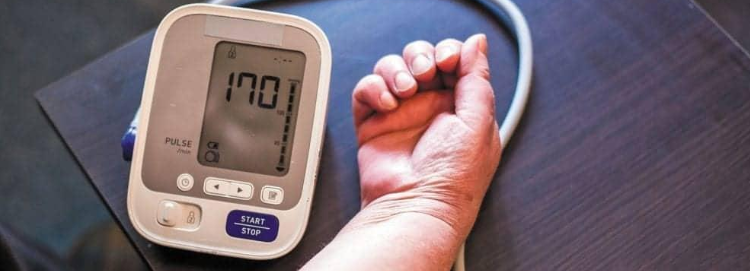
When discussing the negative health impacts of coffee, one of the most frequently mentioned issues is elevated blood pressure. Caffeine causes blood vessels to constrict, affecting all vessels including those supplying blood to the brain. This can result in a temporary increase in your blood pressure. Ideally, your blood pressure should be around 120/80. You can refer to a chart here for detailed explanations of blood pressure levels and acceptable/ideal ranges.
Hypertension can cause damage to both the heart and arteries, raising the risks of stroke, transient ischemic attacks (TIA), and even dementia. However, scientific studies indicate that various other components in coffee might benefit the cardiovascular system, and regular coffee consumption does not contribute to hypertension.
2.Symptoms of Insomnia

Many people believe they understand insomnia, but its symptoms extend far beyond just difficulty sleeping. Insomnia often comes with a host of other problems such as fatigue, difficulty concentrating, increased errors in both professional and personal settings, low energy levels, erratic emotional behavior, depression, and overall reduced performance and cognitive function. When considering the full spectrum of insomnia’s effects, it’s clear that many aspects can be negatively impacted.
Insomnia can be triggered by physical pain or mental health issues like anxiety or depression. If you’re already experiencing anxiety, consuming more caffeine can exacerbate your symptoms and make even simple tasks harder to handle. This can lead to heightened feelings of paranoia, trembling, social anxiety, and general panic.
These issues contribute significant stress to your daily life, forcing your body to work harder than usual and increasing various health risks.
3.Lack of Quality Sleep

While insomnia and caffeine consumption are related, their effects can be entirely separate. One advantage of drinking coffee is that it helps maintain alertness. However, if you have developed a high tolerance for caffeine, it might be due to your regular intake of large amounts of caffeine.
Even if you don’t feel particularly sensitive to caffeine, it doesn’t mean its effects aren’t occurring in your body.
Your brain contains a chemical called adenosine that interacts with receptors on nerve cells, making you feel sleepy. (Receptors are specific proteins on the cell surface that transmit information from outside the cell to inside.) Caffeine binds to these adenosine receptors and prevents adenosine from doing so. As a result, you feel less tired and more alert.
Caffeine can take up to 9 hours to be cleared from your system, which means it can interfere with your sleep for most of that time.
4.Hindering Children’s Growth?

Drinking coffee alone won’t stunt your child’s growth. However, American children often consume large amounts of caffeine through soda and energy drinks daily.
While there’s scant evidence showing that coffee negatively impacts a child’s growth directly, there are more speculations about its effects on behavior or increased anxiety levels; however, research remains limited on this front.
It’s important to note that energy drinks and sodas marketed towards children (which contain high levels of caffeine) are sold in similar quantities as those for adults. Given children’s lower Body Mass Index (BMI), they might end up consuming excessive amounts of caffeine.
Countries like Canada recommend limiting children’s daily caffeine intake to 2.5 mg per kilogram of body weight.
5.Caffeine Withdrawal
If you’re an avid coffee drinker, you might unknowingly develop a dependency on it—certainly not one of its perks. Cutting out caffeine from your diet can lead to what’s known as caffeine withdrawal, which comes with numerous side effects and disruptions throughout the day.
Even if you gradually reduce your coffee intake over time, some issues may still persist.
Firstly, it’s well-documented that caffeine withdrawal can cause headaches—the first noticeable symptom for many people. You’ll feel it behind your eyes, extending across your forehead and eventually reaching your temples. But headaches aren’t the only problem; once they subside, fatigue, difficulty concentrating, anxiety, mild depression, and irritability may follow suit.
Caffeine acts as a stimulant in coffee—a double-edged sword indeed. While you can still reap benefits from chlorogenic acid and other compounds in coffee (which have fewer side effects), the stimulant properties of caffeine impact various muscles in your body—including those in your brain.
A small amount of caffeine might be manageable for your system; however, withdrawal leads to the constriction of these blood vessels.
6.Dehydration
Have you ever noticed that drinking coffee makes you feel even thirstier?
This happens because coffee acts as a diuretic. While this isn’t considered one of coffee’s main benefits, it does mean that it helps your kidneys process extra fluids and sodium, potentially leading to dehydration.
If you’re drinking coffee to compensate for not drinking enough water, it can create a cycle that increases your risk of dehydration. However, this risk is generally low. Drinking a large amount of coffee in one day might leave your lips feeling slightly chapped at most; symptoms like these won’t arise from just one or two cups daily. Increased urination will occur, and if you’re prone to allergies, dehydration might be more likely to happen. This could manifest as sunken eyes, shortness of breath, or excessively dry skin.
Measuring Differences
Ongoing scientific research continues to uncover more about the health benefits and components of coffee. What’s considered “bad” today might be deemed “good” tomorrow (and vice versa). This is the nature of scientific inquiry.
Everyone reacts differently; some people might find they enjoy their afternoon cup even more due to these positive aspects while others might find the downsides intolerable.
In any case, now that you’re informed about these details, you can make better decisions affecting your life accordingly.
